Google Mandiant safety analysts warn of a being concerned new development of risk actors demonstrating a greater capacity to find and exploit zero-day vulnerabilities in tool.
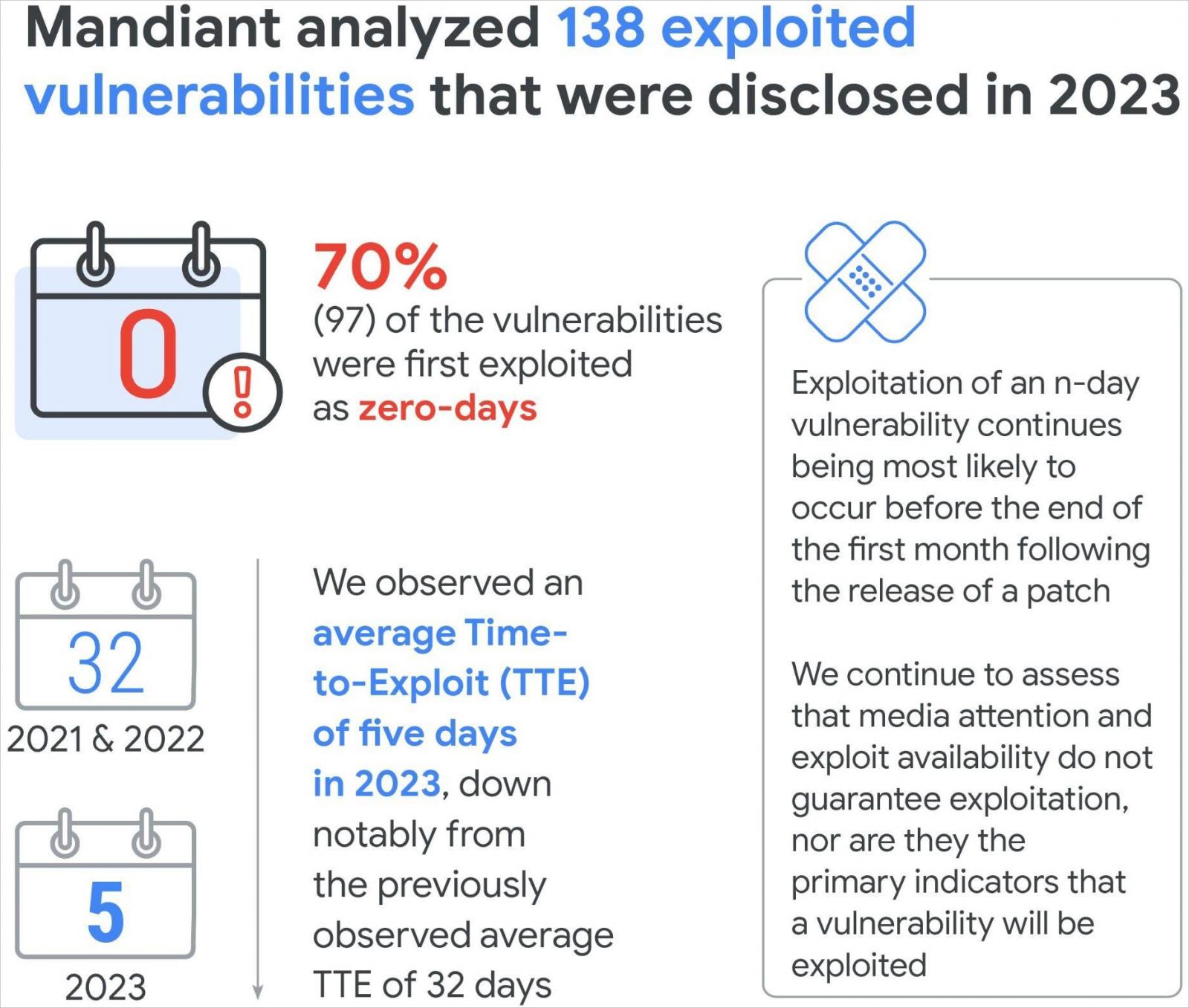
In particular, of the 138 vulnerabilities disclosed as actively exploited in 2023, Mandiant says 97 (70.3%) had been leveraged as zero-days.
Which means risk actors exploited the issues in assaults ahead of the impacted distributors knew of the insects life or were ready to patch them.
From 2020 till 2022, the ratio between n-days (fastened flaws) and zero-days (no repair to be had) remained rather stable at 4:6, however in 2023, the ratio shifted to a few:7.
Google explains that this isn’t because of a drop within the selection of n-days exploited within the wild however quite an build up in zero-day exploitation and the enhanced skill of safety distributors to hit upon it.
This greater malicious task and diversification in focused merchandise could also be mirrored within the selection of distributors impacted by way of actively exploited flaws, which has greater in 2023 to a document 56, up from 44 in 2022 and better than the former document of 48 distributors in 2021.
Reaction instances getting tighter
Some other vital development used to be recorded in regards to the time taken to milk (TTE) a newly disclosed (n-day or 0-day) flaw, which has now dropped to simply 5 days.
For comparability, in 2018-2019, TTE used to be 63 days, and in 2021-2022, TTE used to be 32 days. This gave machine directors a lot of time to plot the applying of patches or put into effect mitigations to safe impacted techniques.
Then again, with the TTE now falling to five days, methods like community segmentation, real-time detection, and pressing patch prioritization grow to be much more important.
On a comparable be aware, Google does now not see a correlation between the disclosure of exploits and TTE.
In 2023, 75% of exploits had been made public ahead of exploitation within the wild had began, and 25% had been launched after hackers had been already leveraging the issues.
Two examples highlighted within the report back to exhibit that there is not any constant courting between public exploit availability and malicious task are CVE-2023-28121 (WordPress plugin) and CVE-2023-27997 (Fortinet FortiOS).
.jpg)
Supply: Google
Within the first case, exploitation began 3 months after disclosure and ten days after a proof-of-concept used to be revealed.
Within the FortiOS case, the flaw used to be weaponized nearly in an instant in public exploits, however the first malicious exploitation tournament used to be recorded 4 months later.
Problem of exploitation, risk actor motivation, goal price, and total assault complexity all play a job in TTE, and an immediate or remoted correlation with PoC availability is incorrect in line with Google.
