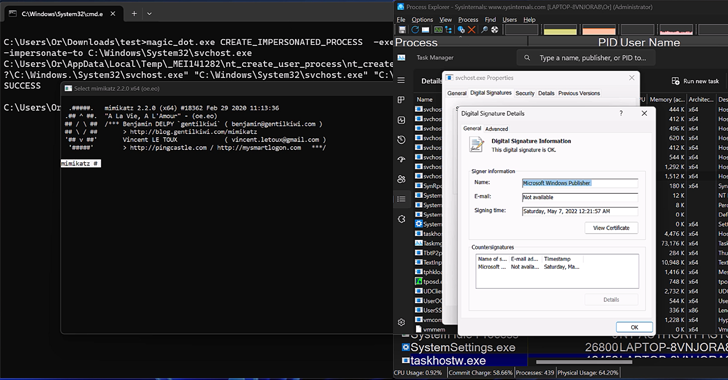
New analysis has discovered that the DOS-to-NT path conversion course of might be exploited by menace actors to realize rootkit-like capabilities to hide and impersonate recordsdata, directories, and processes.
“When a person executes a operate that has a path argument in Home windows, the DOS path at which the file or folder exists is transformed to an NT path,” SafeBreach safety researcher Or Yair mentioned in an evaluation, which was offered on the Black Hat Asia convention final week.
“Throughout this conversion course of, a identified problem exists during which the operate removes trailing dots from any path aspect and any trailing areas from the final path aspect. This motion is accomplished by most user-space APIs in Home windows.”
These so-called MagicDot paths permit for rootkit-like performance that is accessible to any unprivileged person, who might then weaponize them to hold out a sequence of malicious actions with out having admin permissions and stay undetected.

They embrace the power to “disguise recordsdata and processes, disguise recordsdata in archives, have an effect on prefetch file evaluation, make Job Supervisor and Course of Explorer customers suppose a malware file was a verified executable printed by Microsoft, disable Course of Explorer with a denial of service (DoS) vulnerability, and extra.”
The underlying problem throughout the DOS-to-NT path conversion course of has additionally led to the invention of 4 safety shortcomings, three of which have since been addressed by Microsoft –
- An elevation of privilege (EoP) deletion vulnerability that might be used to delete recordsdata with out the required privileges (to be mounted in a future launch)
- An elevation of privilege (EoP) write vulnerability that might be used to write down into recordsdata with out the required privileges by tampering with the restoration means of a earlier model from a quantity shadow copy (CVE-2023-32054, CVSS rating: 7.3)
- A distant code execution (RCE) vulnerability that might be used to create a specifically crafted archive, which may result in code execution when extracting the recordsdata on any location of the attacker’s alternative (CVE-2023-36396, CVSS rating: 7.8)
- A denial-of-service (DoS) vulnerability impacting the Course of Explorer when launching a course of with an executable whose identify is 255 characters lengthy and is and not using a file extension (CVE-2023-42757)
“This analysis is the primary of its variety to discover how identified points that seem like innocent might be exploited to develop vulnerabilities and, in the end, pose a big safety danger,” Yair defined.

“We imagine the implications are related not solely to Microsoft Home windows, which is the world’s most generally used desktop OS, but in addition to all software program distributors, most of whom additionally permit identified points to persist from model to model of their software program.”
